Cat diseases
You know your cat better than anyone, you can see that he is not the same as usual. But it is not always easy to spot a problem. Learn to detect the symptoms, causes and how to treat them.
Symptoms and signs that should alert you
Here are the signs that your pet is probably sick. If you notice that he is losing weight, or on the contrary that he is gaining weight. If he lacks appetite even though he has always eaten properly or if he drinks excessively. If he seems less active to you, he no longer plays and isolates himself. If he urinates often. If he doesn’t purr anymore. These are unmistakable signs that should alert you.
Cat AIDS – Feline Immunodeficiency (FIV)
AIDS or FIV (Feline Immunodeficiency Virus), is a virus that specifically affects the feline breed. It is therefore not transmissible to humans or other animals. It is contagious and transmitted through saliva (bite). Cats living outdoors are most at risk. The observable symptoms are a fever that does not go away, progressive weight loss, anemia, and repeated infections. There is currently no vaccine against FIV.

Feline Calicivirus Virus (FCV)
Calicivirus is caused by the calicivirus, a virus that mainly affects the respiratory tract. It is one of the most serious respiratory infections. Fever, sneezing, conjunctivitis, and more or less purulent discharge from the nostrils are the main symptoms of this chronic disease which is very difficult to stop.

Coryza – Feline Viral Rhinotracheitis (FVR)
Coryza, cat cold or flu, is an extremely contagious infectious disease, also called viral rhinotracheitis. It mainly affects the respiratory system. It can be serious, even fatal, if not treated, and against which it is very important to vaccinate your pet. Runny eyes and nose, sneezing, coughing, fever, and loss of appetite are the most common symptoms.

Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP)
FIP or feline infectious peritonitis is a disease caused by Coronavirus. It is a very serious, incurable, and fatal pathology that mainly affects young people living in communities. The main symptoms are fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, vomiting, diarrhea, and deterioration of the general condition. Unfortunately, there is currently no vaccine against infectious peritonitis.

Feline Leukosis (FeLV)
Feline leukosis is a dreadful, highly contagious viral disease, that has similarities with “cat AIDS” or FIV, but it is not transmissible to humans. It is caused by a virus called feline leukemogenic virus or FeLV. There is a vaccine, 100% effective, and this prevention is essential because there is currently no curative treatment for leukosis. The symptoms are very varied: tumors, swelling of the lymph nodes, loss of appetite, weight loss, fever, and chronic diarrhea.

Feline Typhus Virus – Panleukopenia (FPV)
Typhus is a serious viral infectious disease that can be fatal and is highly contagious. It is also called panleukopenia. It is caused by a parvovirus which causes infectious gastroenteritis. The equivalent in dogs is canine parvovirus. Thanks to vaccination, it is quite rare these days. The main symptoms observed are hemorrhagic diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, severe fatigue, fever, and decreased appetite.
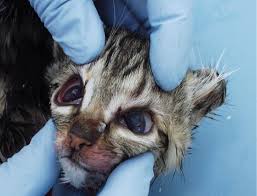
Rabies
Feline rabies is a dreadful disease because it is always fatal and transmissible to humans. There is no curative treatment, but vaccination, which is not obligatory, is recommended and remains the best prevention solution. It is also obligatory when crossing borders. The virus is most often transmitted by bite or scratch from an animal carrying the virus.

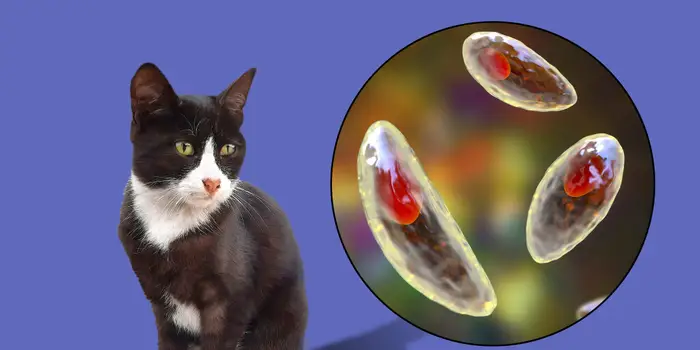
Feline toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a zoonosis, so it is transmissible from animals to humans. It can also occasionally affect the dog. The cat is contaminated by ingesting its prey, rats, field mice, and small birds. Most of the time, the infection goes unnoticed and a healthy pet usually does well. But for kittens or elderly people symptoms may appear, such as severe diarrhea, fever, or difficulty breathing. The animal must then absolutely be taken to your veterinarian.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Create an account or sign in to save pets you love.
Don't have an account? Contact us
Before you proceed with your adoption application, please review and accept our data handling practices:
Note: By clicking "I Agree & Continue", you will be redirected to an external application form. This tracking system logs your interest but does not capture data from the external form.
Create an account or sign in to save pets you love.
Don't have an account? Contact us
Before you proceed with your adoption application, please review and accept our data handling practices:
Note: By clicking "I Agree & Continue", you will be redirected to an external application form. This tracking system logs your interest but does not capture data from the external form.